Many patients do not realize it but the eyes are the only place in the body that we can look directly at the blood vessels to see how they are reacting throughout the rest of their bodies. Therefore, our doctors work very closely with local general practitioners, internists and endocrinologists to manage diabetic eye care. Once we have seen you, we will send a report back to your primary care provider to let them know how your blood vessels are responding to any current treatments. Together, we make a great team responsible for your total care!
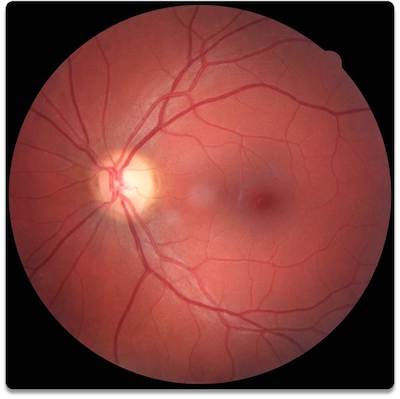
Healthy Eye
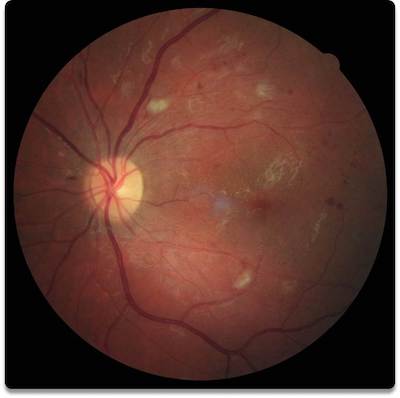
Complications from Diabetes
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes in which causes abnormalities in the tiny blood vessels nourishing the retina. These vessels weaken leak fluid and blood, fail to provide nutrients necessary for good health in the retina. Left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can result in severe visual loss, including blindness.
What is the retina?
The retina is the thin layer of delicate nerve tissue which lines the back of your eye. Light enters the front of the eye and lands on the retina which then sends the image to the brain for processing. When damaged or unhealthy this image will become blurred or distorted.
Diabetic Retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness among adults. Approximately, 25% of current diabetics have some form of the disease. The risk of developing diabetic retinopathy increases with age and the duration of the disease. it is estimated at over 90% of diabetics will experience some form of retinopathy in their lifetime.
Visual symptoms related to Diabetes
- Fluctuating vision in response to changing blood glucose levels; vision can change from day to day, or from morning to evening.
- Blurred central vision from macular edema can interfere with reading.
- Decreased visual acuity can interfere with seeing the markings on an insulin syringe or the display on a standard blood glucose monitor.
- Irregular patches of vision loss or "blind spots" can make it difficult to judge the size of food portions on a plate.
- Decreased depth perception, in combination with decreased visual acuity, can make it difficult to see curbs and steps.
What can I do about it?
Proper blood glucose management is paramount to keeping retinopathy in check. Nutrition and diligent compliance with a primary care physician are the most important factors for ongoing wellness.
